Our earth is not a static planet, it is a dynamic planet. There are constantly undergoing changes inside and outside of the earth.
- Crust
- Mantle
- Core
- The uppermost layer of the earth is called the crust.
- It is about 1 % of eath masses
- The crust is the thinnest of all layers of the earth.
- It is about 35 km in-depth on the continental masses.
- It is about 5 km in-depth on the ocean passes.
- The crust can be divided into two major groups Continental crust and Oceanic crust.
- Continental crust is comprised of two major minerals- Silica and Alumina ( Silica and Aluminum). It is also called SiAl.
- Oceanic crust is comprised of two major minerals-Silica and magnesium. It is also called SiMa ( Silica and Magnesium).
- The mantle is just beneath the crust; it extends up to the depth of 2900 Km below the crust.
- It is about 84 % of the earth's mass.
Core:
- The core is an innermost layer
- The radius of the Core is about 3500 Km
- It is mainly made up of NiFe(Nickel and ferrous).
- The core of the earth is divided into two parts-Outer core and the Inner core.
- The outer core is in a semi-liquid state.
- The central core has very high temperature and pressure and it is solid form.
- Core makes 15 % of the total volume of the earth.
- Any natural mass of minerals matter that makes up the earth's crust[ outermost layer of the earth] is called a rock.
- Earth's crust is made up of various types of rocks.
- Rocks can be of different colors, sizes, and textures.
There are three major types of rocks:
- Igneous rocks
- Metamorphic rocks
- Sedimentary
There are two types of Igneous rocks:
- Intrusive rocks
- Extrusive rocks
When molten magma cools down deep inside the earth's crust; called intrusive rocks. Since they cool down slowly they form large grains, for example, Granite rocks.
Extrusive rocks:
- When molten lava comes out on the earth's surface, it cools down very fast and becomes solid, which are called extrusive rocks. Extrusive rocks have a very fine-grained structure.
- For example, Basalt rocks are extrusive rocks and Deccan Plateaus are made up of basalt extrusive rocks.
Sedimentary rocks:
- Small particles of rocks are called sediments.
- These sediments are transported and deposited by winds, water, wave, etc.
- These sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks.
- The process of the formation of layered rocks is called the sedimentation process. Rocks formed by the sedimentation process are called sedimentary rocks.
- These rocks contain fossils of plants and animals.
- It is also a source of Petroleum, coal, and natural Gases.
- Sandstone is made up of sand grains and is a sedimentary rock.
Metamorphic rocks:
Under great heat and pressure, Igneous and Sedimentary rocks change into metamorphic rocks.
For example,
- Clay changes to Slate( a metamorphic rock)
- Limestone changes to Marble( a metamorphic rock)
Uses of rocks:
The following are uses:
- Hard rocks are used for making roads, houses, and many infrastructures.
- Redfort is made up of Red Sandstone( i.e sedimentary rocks)
- Taj Mahal is made up of white marble( i.e Metamorphic rocks)
- Rocks are the sources of Mineral for industries use
- Metamorphic rocks are the source of Fossil fuels.
- One type of rock that can be changed to other types under certain conditions in the cyclic matter is called the rock cycle.
- The process of transportation of the rock from one to another is called the rock cycle.
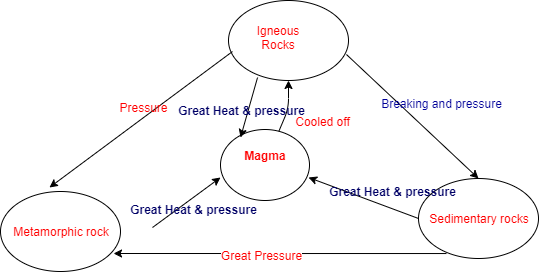 |
| Rock cycle |
- The following are the three layers:
- Crust
- Mantle
- Core
- Any natural mass of minerals matter that makes up the earth's crust is called a rock. Earth's crust is made up of many types of rocks.
- Igneous rocks
- Metamorphic rocks
- Sedimentary
When molten magma cools down deep inside the earth's crust; called intrusive rocks. Since they cool down slowly they form large grains, for example, Granite rocks.
Extrusive rocks:
- When molten lava comes out on the earth's surface, it cools down very fast and becomes solid, which are called extrusive rocks. Extrusive rocks have a very fine-grained structure.
- For example, Basalt rocks are extrusive rocks and Deccan Plateaus are made up of basalt extrusive rocks.
- Hard rocks are used for making roads, houses, and many infrastructures.
- Redfort is made up of Red Sandstone( i.e sedimentary rocks)
- Taj Mahal is made up of white marble( i.e Metamorphic rocks)
- Rocks are the sources of Mineral for industries use
- Metamorphic rocks are the source of Fossil fuels.
For example,
- Clay changes to Slate metamorphic rocks.
- Limestone changes to Marble metamorphic rocks.
1. Deepest mine of the earth is located in which country?
a) Russia
b) Canada
c) South Africa
d) Australia
Answer. c) South Africa. The deepest mine is in South Africa; it is about 4 km deep.
2. What is the average depth of continental crust?
a) 5 km
b) 29 km
c) 35 km
d) 54 km
Answer. c) 35 km
3. What is the average depth of oceanic crust?
a) 5 km
b) 29 km
c) 35 km
d) 54 km
Answer. a) 5 km
4. What is the radius of the earth?
a) 2900 km
b) 3500 km
c) 6371 Km
d) 12069 km
Answer. c) 6371 Km
5. The rock which is made up of molten magma is
a) Igneous
b) Sedimentary
c) Metamorphic
d) Secondary rock
Answer. a. Igneous
Igneous rock forms after the cooling of molten magma. Igneous rock is also called primary rock.
The loose materials of rocks are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks, this type of rock is called sedimentary rock.
Under great heat and pressure, igneous and metamorphic rocks get converted to other forms of rock is called metamorphic rock.
6. The innermost layer of the earth is
a) Crust
b) Core
c) Mantle
d) Lithosphere
Answer. b. Core.
The innermost layer of the earth is called the Core.
The radius of the core is about 3500 km and it is made up of NiFe( nickel and ferrous).
7. Gold, petroleum, and coal are examples of
a) Rocks
b) Minerals
c) Fossils
d) Fuels
Answer. b. Minerals
Minerals are a kind of rock that has definite physical properties and define chemical composition.
Gold, petroleum, and coal are examples of Minerals.
8. Rocks that contain fossils are
a) Sedimentary rocks
b) Metamorphic rocks
c) Igneous rocks
d) Primary rocks
Answer. a. Sedimentary rocks.
Sedimentary rocks are made up of layers and between the layer, they contained fossils of plants, animals, microorganisms.
9. The thinnest layer of the earth is
a) Crust
b) Mantle
c) Inner Core
d) Outer Core
Answer. a. Crust.
The thinnest layer of the earth is called the crust.
Crust: It is around 35 km on continents and 5 km on the ocean.
Mantle: 2900 km
Core: 3500 km
10. Continental crust is made up mainly?
a) SiAl
b) SiMa
c) Nife
d) Metamorphic rocks
Answer. a) SiAl
11. Oceanic crust is mainly made up by?
a) SiAl
b) SiMa
c) Nife
d) Metamorphic rocks
Answer. b) SiMa
12. Core is mainly made up by?
a) SiAl
b) SiMa
c) Nife
d) Metamorphic rocks
Answer. c) Nife
13. Which of the following is an example of Igneous rock?
a) Basalt rocks
b) Marble
c) Sandstone
d) Slate
Answer. a) Basalt rocks
14. Which of the following is an example of Sedimentary rock?
a) Basalt rocks
b) Marble
c) Sandstone
d) Slate
Answer. c) Sandstone
a) Basalt rock
b) Granite
c) Slate
d) Marble
Answer. a) Basalt rocks
16. Which of the following is known as a primary rock?
a) Igneous rock
b) Sedimentary rock
c) Metamorphic rock
d) Marble
Answer. a) Igneous rock
17. Which of the following rock may contain the fossil remains?
a) Igneous rock
b) Sedimentary rock
c) Metamorphic rock
d) Marble
Answer. b) Sedimentary rock
18. The rock which has a layered structure?
a) Igneous rock
b) Sedimentary rock
c) Metamorphic rock
d) Marble
Answer. b) Sedimentary rock
19. What is the radius of the earth's core?
a) 2900 km
b) 3500 km
c) 6371 km
d) 100 km
Answer. b) 3500 km
20. What is the width of the earth's mantle?
a) 2900 km
b) 3500 km
c) 6371 km
d) 100 km
Answer. a) 2900 km
21. Which of the following rocks is an example of Intrusive Igneous rock?
a) Basalt rock
b) Granite
c) Slate
d) Marble
Answer. b) Granite
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon