Freshwater sources:
- Glaciers and icecaps: 2 % of earth water.
- Groundwater: 0.68 %
- Lake & Ponds: 0.009 %
- Atmosphere: 0.0019 %
- River: 0.0001 %
Salinity:
Salinity is the amount of salt in gram present in 1000 grams of water. The average salinity of ocean water is around 35 parts per thousand.
The salinity of the dead sea in Israel is approx. 340 grams per 1000 grams of water.
Ocean Circulation:
The movement that occurs in the ocean can be broadly categorized as Wave, Tides, and Current.
Wave:
Waves are formed when winds press across the ocean surface. The stronger the winds blow, the bigger the wave generates. Rise and fall of ocean water alternatively are called a wave.
During storms; high-speed winds form huge waves.
Earthquake, volcanic eruption or landslide underwater can shift a large amount of water called Tsunami. t is a very high tide wave around 15 m high and does large destruction along the coast.
Tides:
Rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called Tide.
Types of tides:
Two types
- Neap Tide
- Springtide; It has during a full moon and new moon days.
Uses of High Tides:
- It helps in navigation
- It helps large ships to reach the harbor
- Fishing
- To generate electricity.
Ocean Currents:
Ocean currents are streams of water flowing in definite directions. There are two types of ocean current:
- Warm Current
- Cold current
Warm Ocean current:
Originates near the equator and move towards the poles.
For example Gulf Stream current.
Cold current:
Carry water from poles or higher latitudes to lower latitudes.
For examples, Labrador ocean current
Fishing hots spots: The region where hot and cold water currents meet is the best fishing ground in the world. It also makes foggy weather; it makes difficulty in navigation.
For example, Area around Japan, Eastern coast of America.
Exercises
Q1. What is precipitation?
Answer.
When Moisture in the air not able to hold more water and it falls under gravity in the form of water, snow, and hails; is called precipitation.
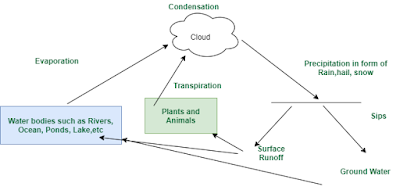
Q2. What is the water cycle?
Answer.
Water circulates one form to others( liquid, water vapor), and from lands to the atmosphere in a cyclic manner is called the water cycle. The following diagram shows the water cycle.
Q3. What are the factors affecting the height of the waves?
Answer.
The following factors affecting the height of waves:
Winds speed
Water depth
Surface topography of water
Winds direction
Q4. Which factors affect the movement of ocean water?
Answer.
The following factors affect:
Ocean Salinity
Ocean temperature
Winds Speed
Ocean Depth and topography
Q5. What are tides and how are they caused?
Answer.
The rise and falls of ocean water twice a day is called tides. They are caused by the gravitation pull of the Moon and Sun.
Q6. What are ocean currents?
Answer.
Ocean currents are the stream of water flowing in a particular definite direction. It may be a warm or cold current.
| 
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon