Channel morphology
Channel morphology is also called river channel morphology, it is a complete study of the channel from the geography aspect to the channel fluids dynamics aspect.
The following are the major components of Channel Morphology:
Channel geometry
Hydraulic geometry
River or Channel bed confirmation
River or channel pattern
Channel types
Hydraulic geometry
River or Channel bed confirmation
River or channel pattern
Channel types
Channel fluid dynamics
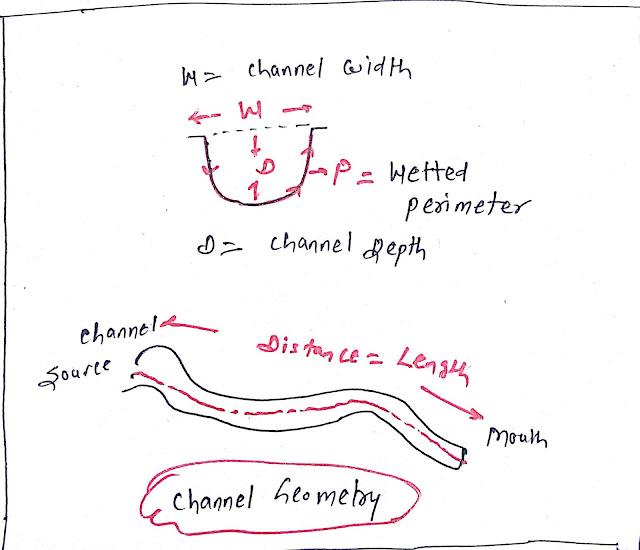
Channel geometry:
It includes the study or measurement of the following:
It includes the study or measurement of the following:
- Channel length
- Channel width
- Channel depth
- Wetted perimeter
- Channel thalwegs
Channel Length:
Distance from the river source to the mouth of the river.
Channel width:
- The straight cross-sectional distance of the channel is called channel width. Channel width varies with the volume of water seasonally.
- In India, the maximum width of the river channel can be measured in monsoon seasons.
Channel depth:
It is measured as the vertical distance from the river water surface to the maximum bed depth.
It is measured as the vertical distance from the river water surface to the maximum bed depth.
Wetted perimeter:
It is measured by the cross-sectional distance of the wetted portion of valleys.
It is measured by the cross-sectional distance of the wetted portion of valleys.
Channel thalwegs:
It represents the line connected with all the maximum depth of water from the source to the mouth of the channel.
It represents the line connected with all the maximum depth of water from the source to the mouth of the channel.
Channel bed topography
It refers to the study of erosional and deposition features present such as sand bars, sand dunes, potholes, plunge pools, etc in the river bed and how these features interact with the river fluid such as water and river sediments.
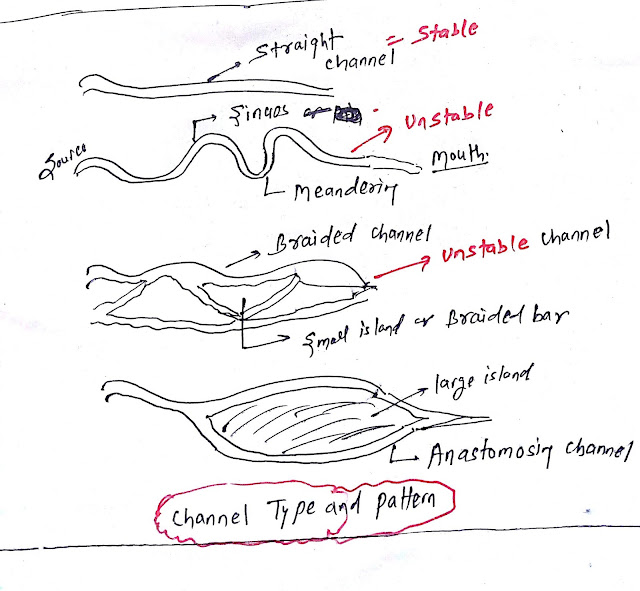
Channel pattern
The following is the pattern of the Channel:
- Straight channel
- Sinuous or Meandering channel
- Braided channel: two more channels with a braided bar and a small island.
- Anatomic channel: two or more channels with large stable islands.
 |
| Channel Pattern and Types |
Channel types
There are two types of channels.- Stable channel
- Unstable channel
The straight channel is generally a stable channel as compared to the braided channel. The position of braided bars and islands changes frequently in braided channels hence it is called the unstable channel.
Channel fluid dynamics:
Study of channel fluid dynamics such as channel discharge capacity, channel velocity, sedimentary load capacity, transportation capacity, etc.
You may like also:
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon