Secondary winds are seasonal in nature, and do not continuously flow in the same direction throughout the year as planetary winds blow. Secondary Winds also do not blow extensively in the large distance as primary winds blow.
The following are secondary winds:
The following are secondary winds:
- Monsoon winds.
- Land breezes
- Sea breezes
- Mountain winds
- Urban wind cells
Monsoon winds:
On 21 June, Sunray makes 90 degrees on the tropic of cancer, hence the air rise, and low pressure is created over Indian plains and high pressure is created over the Indian ocean. Air moving from High-pressure regions toward the Indian subcontinent is called monsoon winds.
On 22 December, the situation is reversed. Sunray is longitudinal in the tropic of Capricorn. Low pressure is created over the Indian Ocean and High Pressure is Created over the Indian Subcontinent, Air moves from the high-pressure region over the Indian subcontinent toward the Indian ocean.
Land breezes:
In coastal areas region up to 50 Kilo Meter from the ocean, during the night, the land cools sharply as compared to the sea, hence the low-pressure area is created on the sea and air moving from land to sea are called land breezes. Winds are dry and winds reach Up to 40 to 50 in ocean areas. |
| Land and Sea Breeze |
Sea Breezes:
During the day in coastal areas region, the land is heated sharply as compared to the sea and low-pressure areas are created on land and high-pressure areas in the sea. Winds that blow from sea to land during the day are called sea breezes. Winds are wet and winds reach Up to 40 to 50 km from interior to coastal areas.
Valley Breezes:
In the mountainous region, During the day, valleys and mountain slopes get heated sharply as compared to the mountain top. Winds from the valley to the upland are called valleys breezes.
Valley and mountain breezes:
In the mountain region:Valley has water bodies, rivers, and also the vegetation. So, it heats and cools slowly.
In summits, there are no water bodies, and very little vegetation or vegetation is absent, hence heats sharply during the day and cools fastly during the night.
- During the night, high pressure is created in the mountain summit, and low pressure is created in valleys.
- Winds that Flow from mountain summit to valleys is called Katabatic winds. It is very cold.
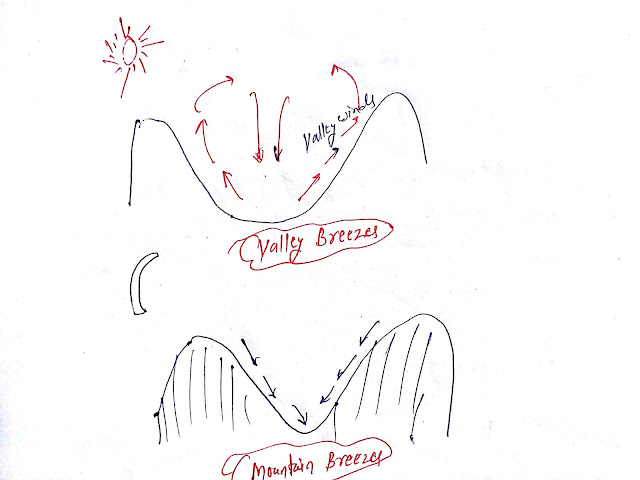 |
| Mountains and Valley Breezes |
Valley Breezes:
- During the day, due to intense heat, there will be low pressure at the mountain summit and high pressure at valleys, hence winds will flow from valleys to the mountain summit, which is called valley breezes.
Urban wind cells:
In urban areas, low pressure is created throughout the years due to factories' emissions, transportation emissions, pollution, overpopulation, cementing of the floor, etc.Due to low-pressure air rise and winds coming from the surrounding region and making a close cell is called the urban winds cell.
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon