Overall nutrients( Carbon, nitrogen, calcium, sulfur, etc,) in ecosystems remain the same, they are never lost, and it recycled over time again and again. The movement of nutrients elements through the various components of an ecosystem is called the nutrients cycle or Biogeochemical cycle. It is called biogeochemical because these chemical moves from abiotic components( air, earth crust, water) to biotic components( plants and animal).
Biogeochemical cycles are of two types;
Gaseous Cycle
- The reservoir of Gaseous such as Carbon and Nitrogen in the atmosphere.
Sedimentary cycle:
- The reservoir of sediments such as Sulphur and Phosphorous is soil.
Carbon Cycle:
The following is some information about carbon.
- In the dry weight of organisms, carbon contains 49 %.
- 71 % of global carbon is dissolved in oceans.
- Ocean reservoirs regulate the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Our atmosphere contains only 1 % of global carbon.
About the carbon cycle:
- Carbon is fixed in the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
- Carbon is released into the atmosphere by the respiration activities of organisms.
- Carbon is also released into the atmosphere by burning wood, forest fire, industrial processing, and combustion of fossil fuels and organic matter.
- A decomposer is also released carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through the mineralization process.
- Carbon is also added to the soil by the decomposition of dead organisms.
Nitrogen Cycle:
- Nitrogen is the most prominent gas in the atmosphere, it comprises 71 % of the total composition of the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen is found in protein, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, green leaves, or Chlorophylls.
- The plant can not take nitrogen from the atmosphere directly. Plants take nitrogen from ammonia, nitrites, or nitrates.
- Naturally, nitrogen gets fixed from the atmosphere in two ways:
- Nitrogen gets converted to nitrogen oxides ( NO, NO2) through lightening.
- Some microorganisms such as bacteria and green algae fix the nitrogen to ammonia( NH3).
- Rhizobium ( symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria) fixes the nitrogen in association with leguminous plants.
- Some bacteria present in soil release nitrogen through denitrification.
- Atmospheric nitrogen oxides get released by industrial combustions, automobiles, and forest fires.
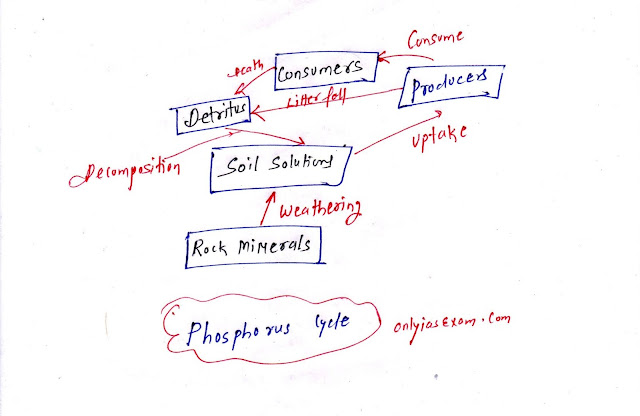
Phosphorus cycle;
- Phosphorous helps the information of Nucleus acid and cellular energy of the organism.
- Many animals need phosphorus to make shells, bones, and teeth.
- The natural reservoir of phosphorus is the rock.
- Phosphorus gets dissolved in the water after weathering of rocks.
- From soil, it reaches plants.
- Dead plants and animals are decomposed and decomposer bacteria released the phosphorous.
- There is the respiratory release of phosphorus into the atmosphere.
Sulfur cycle:
- Soil and sediments of coal and rocks are reservoirs of sulfur.
- Sulfur is also present in the food chain in form of protein and amino acids.
- Sulfur is also present in the atmosphere in form of Sulfur dioxide (So2) and Hydrogen Sulphide( H2S).
- Combustion of fossil fuel, industrial processing, and volcanic eruption are the major sources of sulfur release in the atmosphere.
- Through rainwater in the form of acid rain or sulphuric acid, it came back into the soil from the atmosphere.
You may like also:
- पारिस्थितिकी का सिद्धांत
- Principle of Ecology
- Principle of ecology UPSC | Environmental Geography
- Principle of Ecotone and Ecocline
- Principle of biomass productivity
- Principle of Symbiosis relationship between the living organism
- Principle of Ecological Succession
- Principle of energy flow| Principle of Trophic level
- Principle of Biogeochemical cycles



ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon