Table of Contents:
- Arid Landforms and process
- Deflation
- Abrasion
- Attrition
- The erosional landform in the desert
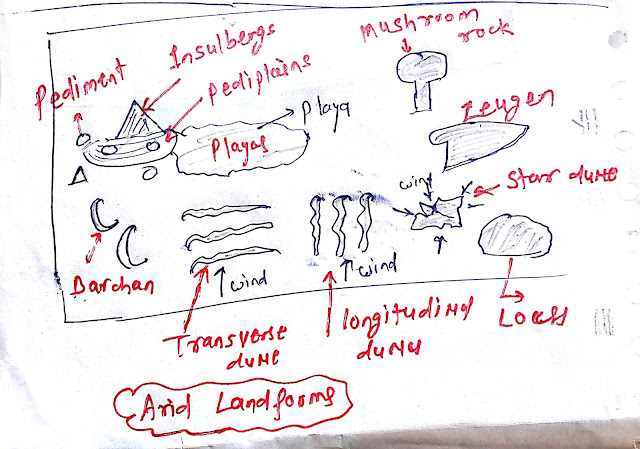
- Pediment
- Inselbergs
- Zeugen
- Pediplains
- Balson
- Deflection basin or blowout
- Playas
- Mushroom rock
- The depositional landform in the desert
- Ripple marks
- Sand dune
- Longitudinal dunes.
- Transverse dunes.
- Crescent-shaped
- Star-shaped dunes
- Loess
Arid Landforms
Landforms are created in the arid region mostly by winds. Some landforms are also developed by water.
There are three processes involved by air in the creation of arid landform:Deflation:
- Removing, lifting, and transporting sands and dust particles away by winds is called deflation.
Abrasion:
- When the sand and dust-loaded winds erode the wall of rocks by grinding is called abrasion.
Attrition:
- While transportation, wear, and tear of sand and dust particles are called attrition.
 |
| Arid Landforms |
The erosional landform in the desert:
Pediment:
- The rocky floor at mountain feet with or without a thin cover of debris is called pediment.
- After erosion, weathered rocks or boulders in the arid region are called a pediment.
- It is an isolated hill or small mountain in the arid region.
Zeugen:
- A table-shaped area of rock where softer rocks around it are eroded by winds.
- Valleys in arid landforms
Pediplain:
- High relief in desert areas is reduced to low featureless plains called Pediplains.
Playas:
- Shallow lakes are called players where water is retained only for a short duration due to evaporation. Playas contain good deposition of salt, this cover-up salt is called alkali flat. Salt and sand deposits in Balson areas of desert.
Deflection basin or blow out:
- Depression is made by the deflection process. Sometimes, the depth of this depression may go below sea level.
Mushroom rock:
- The wind is the active agent of erosion and deposition in the desert ecosystem. When the winds erode the lower section of rocks more than the upper part of rocks; rocks left with mushroom-like structures with a narrow base and wider top; are called mushroom rock.
The depositional landform in the desert:
Ripple marks:
The deposition of sands in the en surface like ripple is called ripple marks.
Sand Dunes:
When winds blow in the desert ecosystem, it takes sand with them and transports it from one place to another place. When winds stop blowing, the sand fall and get deposited in a low hill-like structure called sand dunes.
The heap of sands in the desert is called sand dunes.
They are types of sand dunes.
The heap of sands in the desert is called sand dunes.
They are types of sand dunes.
- Longitudinal dunes.
- Transverse dunes.
- Crescent-shaped
- Star-shaped dunes
Longitudinal dunes formed parallel to wind dunes.
Transverse dunes formed perpendicular to the wind direction.
Sand dunes formed are crescent-shaped.
Starlike shapes with high central portions dunes are called star dunes.
Transverse dunes formed perpendicular to the wind direction.
Sand dunes formed are crescent-shaped.
Starlike shapes with high central portions dunes are called star dunes.
Loess
When sands are deposited in large areas in an unsorted way; it is called loess
Try to solve the following question:
- Give a reasoned account of the development of landforms in an arid region. ( UPPSC 1997)
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon