Table of Contents:
- Glacial Landforms
- Erosional landforms by Glaciers
- Cirques
- Torn Lake
- Arete
- Horns
- Cole
- Nunatak
- U shaped Valleys
- Hanging Glacial Valley
- Depositional landforms by Glaciers
- Moraine
- Eskers
- Drumlins
- Basket of Egg topography
- Outwash plains
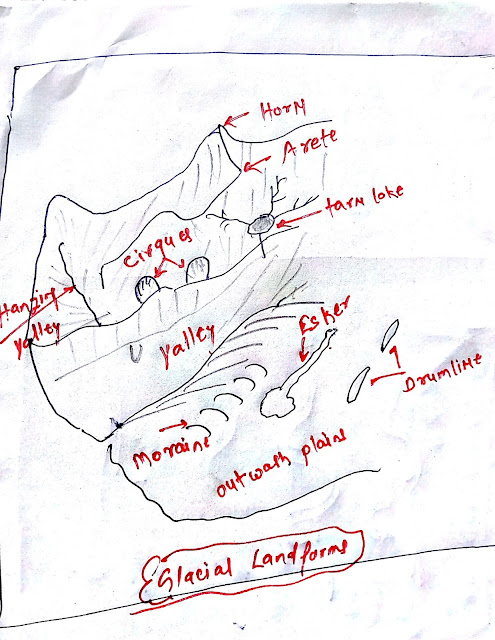
Glacial Landforms
Glaciers are the "river of ice" that too erode the landscape by bulldozing soils and stones to expose the solid rocks from below.
A beautiful lake in the mountains is created when the ice melts.
Masses of moving ice can be two types:- Moving as sheet called continental or piedmont of the glacier. At the foot of the mountain, ice is spread over plains.
- Linear flow down the slopes of the mountain is called mountain or valley glaciers.
Glaciers are slow ( few centimeters to few meters a day, it is not fast as water movement.
Glaciers move because of the force of gravity.
Erosion by glaciers is high because of friction caused by the weight of ice. Glaciers can cause great damage to in weathered rocks and can reduce High mountain to low hills or plains.
Glaciers move because of the force of gravity.
Erosion by glaciers is high because of friction caused by the weight of ice. Glaciers can cause great damage to in weathered rocks and can reduce High mountain to low hills or plains.
 |
| Glacial Landforms |
Erosional landforms by Glaciers:
Cirques:- Cirque is often found at the head of the glacial valley.
- Accumulated ice cut the cirque on the way moving down the mountain valley.
- Cirque is a deep, long, and wide trough with steep walls on the sides.
- A lake of water can be seen within cirque such lakes are called cirque or torn lake.
Arete has two steeper slopes that are made up of backward retreat of two cirques; one from each side. On the top of Arte, it looks like the line.
A hole is developed in glacial mountains by the backward retreat of two cirques by the opposite side of glacial mountains. The hole is called Cole landforms.
Nunatak:
Nunatak is a highland in the glacial region with two steeper sides created by glacial erosion.
Glacial valley:
- High sharp-pointed and steep sides peak is called horns landforms. It is built by the backward retreat of cirques on all sides of the glacial mountains.
A hole is developed in glacial mountains by the backward retreat of two cirques by the opposite side of glacial mountains. The hole is called Cole landforms.
Nunatak:
Nunatak is a highland in the glacial region with two steeper sides created by glacial erosion.
Glacial valley:
- Glacial valleys are U-shaped with broad floor and relatively smooth and steep sides; created by lateral glacial erosion.
- Valley may contain debris comprised of moraines with swamps appearance.
Depositional landforms:
Coarse and fine debris dropped by melting glaciers are called glacial tills.
Moraine:
Moraine:
- The materials carried by the glacier such as big rocks, small rocks, sand, and silt get deposited in the lower part of glacial mountains; these deposits form Glacial Moraines. Moraines are a long ridge of deposits of glacial till.
Eskers:
- When glaciers melt in summer, the water flow on the surface of the ice. Very coarse materials like boulder and block with minor fracture of rocks debris settled in the valley of ice. Ice melt can be found as a sinuous ridge called eskers.
Drumlins:
Outwash plains:
For Explanation, please watch the below videos:
- Smooth oval-shaped ridge-like features composed mainly of glacial till with sand and gravel. Oval or egg-shaped deposits of the glacial moraine are called drumlins.
Many drumlins make the basket of egg topography or basket of egg landscape.
Outwash plains:
- When eroded glacial melts and leave the debris, clay, sand deposited on the surface, it is called outwash plains.
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon