Brief about Von Thunen and his "A Model of Agricultural Land Use":
- Von Thunen [ 1783- 1850] was a German geographer and economist.
- He gave "A Model of Agricultural Land Use" in 1826 which was translated into English in 1966.
- Von Thunen's model of agriculture use is also called the "concept of locational rent".
- His model is based on the study of an agriculture field in Germany.
- In this model, he assumed that a city [ market] is located centrally within an "Isolated State" and the state is self-sufficient in agricultural goods and has no external trade.
- As per Von Thunen, in order to maximize the profit the farmer, 6 concentric rings
- It also explains the hierarchy of agricultural crops based on profit-making capacity.
- Bulky agricultural goods will be produced near the city as it would save the transportation cost by carrying less distance to the city.
- Perishable crops such as vegetables and milk products will also be produced near the city.
- Lightweight and durable agricultural goods such as rice, wheat, etc will be grown far away from the city.
- High profitable crops such as vegetables and fruits will grow near the city as land rent is generally high near the city.
- Rent of land decreases with increasing distance from the Market to the hinterland.
- An intensive method of cultivation is practiced near to market in order to manage the high cost of land and to enhance profitability.
We will discuss Von Thunen's -"A Model of Agricultural Land Use" in detail here, but first, the following basic terminology needs to understand for a better understanding of the model.
- Crop Productivity
- Crop intensity or intensive farming
- Extensive farming
- Mixed cropping
- Hinterland
- Isolated state
Crop productivity:
Crop Productivity = (Production Value / Input Cost) per unit land area.
For example,
- If when we grow wheat on 1 hectare of land, it costs Rs 10 to grow 100 rupees of wheat, then the productivity of wheat will be 100/10 = 10 per hectare.
- On 1 hectare of land on the same land, when we grow chilies, it costs Rs 12 to grow chilies by Rs 200, then the productivity of chilies comes to 200/12 = 16.67
- We can say that the productivity of chili is higher than that of wheat.
Crop intensity or intensive farming:
If two or more crops are grown a year of particular agricultural land, it is called intensive farming. The large level of inputs such as fertilizer, pesticides, labor, and others are used to get a high yield per unit of agricultural land.
Extensive farming:
Extensive farming is a farm practice where less than two crops in a year are cropped. Low levels of inputs are used as compared to intensive farming. There is low productivity in extensive farming as compared to intensive farming.Mixed cropping:
Mixed cropping is a farm practice where two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same piece of land.
For example,
- Growing wheat and grams crops on the same field at the same time
Hinterland:
- An area that is far away from the coastline or river.
Concept of Isolated state in the Von Thunen Model:
- An isolated state is a region that is completely flat.
- And, there is equal soil fertility and climate all over the region.
- And, there is no river or mountains.
- And, the state is self-sufficient in food grains production and there are no trades from outside.
What are the Basic Assumptions in the Von Thunen Model?:
The following are the basic assumption in the Von Thunen Model:
- He made the concept of an Isolated state.
- The isolated state is comprised of one market area[city] and the market is surrounded by flat agricultural land[i.e hinterland].
- The market receives goods only from the hinterland and the hinterland sells goods only to the market.
- Farmers are settled in the hinterland who wish to maximize their profit.
- There is only one mode of transport and the horse wagon is used.
- The market is not accessible by waterway and there is no road.
- Transportation cost is directly proportional to the distance and weight of materials.
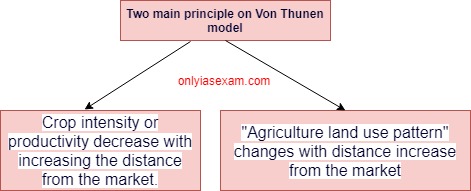
There are two main principles in the Von Thunen model.
- Crop intensity decreases with increasing the distance from the market. The productivity of crops also decreases with increasing the distance from the market.
- "Agriculture land use pattern" changes with the distance increase from the market.
 |
| Von Thunen's model of agriculture |
Locational rent concept:
- Using these two principles and basic assumptions, the Von Thunen model tried to give the optimal land use pattern which will give farmers maximum profit or locational rent.
- Since a farmer is an economic person and hence they will farm those crops which will give more total profit or rent.
Von Thunen also deduce the formula for calculating the locational rent which is given below:
 |
| Von Thunen's total profit calculating the formula |
Since farmers are economic people, they try to minimize the "KM" and want to maximize productivity by adding labor, fertilizer, pesticide, good quality seeds, etc.
For example,
- Vegetables such as tomatoes are perishable items and they are also bulky, which is why tomatoes should be grown near the market area.
As per Von Thunen, the following is the hierarchy of agriculture crops based on profitability in decreasing order:
- Fruits and vegetation [ very high profitability]
- Dairying
- Mixed crop and livestock farming
- Wheat farming
- Ranching[lowest]
What occupies each ring of the Von Thunen model and why?
Considering the locational rent of lands, productivity, weight of items[ bulky or lightweight], and perishable nature of the product, the Von Thunen divided 6 agriculture zone around the market.
 |
| Von Thunen Agriculture Zone |
- Zone1: Land used for growing perishable goods like vegetables, milk, fruits
- Zone 2: Land used for growing forests and timber.
- Zone 3: Land used for growing medium-intensity crops such as vegetable oil.
- Zone 4: Land used for growing low-intensity and durable crops such as wheat, rice, barley, meat,
- Zone 5: Land follows a three-field crop system:
- 1/3 of the area is used for growing crops.
- 1/3 of the area is used for grassland.
- 1/3 of the area is left un-cropped.
- Zone 6. The land is used for ranching and Livestock.
Relevance of Von Thunen’s model of agricultural location in the present context?
Today, the Von Thunen model is not relevant in most parts of the world because of the following reasons:
- An isolated state is not available in any part of the world today.
- Nowadays, the economic rent of land is not only decided by the distance from the market but also by many factors such as nearness to communication networks, climate, relief, safety, etc.
- There are many market centers in a region and the size and influence of the market center change over time.
- Due to technological advancements in the transport, preservation, and packaging field, perishable and bulky items are easily available from the distanced place.
- For example, Amul milk and milk products can be purchased all over India irrespective of the source of production.
However, Von Thunen is still relevant to those places that were lacking in transport and preservation facilities.
Try to solve the following questions:
- Discuss Von Thunen’s model of agricultural land use and examine if the model is applicable to India. (UPSC 1994, 20 marks)
- Discuss the relevance of Von Thunen’s model of agricultural location in the contemporary context. (UPSC 2015, 15 marks)
- Write notes on the relevance of Von Thunen's agricultural location theory in the present context. ( UPSC 2020, 10 Marks)
- Explain the relevance and applicability of Von Thunen's theory of agriculture location in today's world. ( UPSC 2022, 15 Marks)
Answer the following multiple-choice questions on the locational theory of geography:
1. Which of the following gave the concept of "Economic rent"?
a) Ricardo
b) Von Thunen
c) Alfred Weber
d) August Losch
Answer. a) Ricardo gave the concept of economic rent.
2. Which of the following gave the concept of "Locational rent"?
a) Ricardo
b) Von Thunen
c) Alfred Weber
d) August Losch
Answer. b) Von Thunen gave the concept of locational rent.
3. Which of the following gave the concept of least cost theory?
a) Ricardo
b) Von Thunen
c) Alfred Weber
d) August Losch
Answer. c) Alfred Weber
4. Which of the following gave the concept of "profit maximization theory"?
a) Ricardo
b) Von Thunen
c) Alfred Weber
d) August Losch
Answer. d) August Losch gave the concept of "profit maximization theory".
5. Von Thunen model is?
a) Agricultural land use Model
b) Industrial location model
c) Urban land use model
d) Rural settlement
Answer: a) Agricultural land use Model
You may like also:
- वॉन थुनेन - कृषि भूमि उपयोग का एक मॉडल
- World agriculture: a typology of agricultural regions
- What is the meaning of agricultural Productivity? Mention the method of measurement of agricultural productivity adopted by Mohammad Shafi.
- Agricultural Productivity | Agricultural Efficiency| Agricultural Productivity vs Agricultural Efficiency
- Agricultural inputs and productivity
- Agriculture Sector status, role, problems, and step taken by the Indian government
- Agricultural intensity
- कृषि उत्पादकता का क्या अर्थ है ? मोहम्मद सफी द्वारा अपनाई गयी कृषि उत्पादकता निर्धारण की विधि का उल्लेख कीजिये।
- Mention the Agricultural regions of India and give a detailed description of anyone.
- Present a classification of Agricultural Regions of the world developed by Whittlesey.
- World agriculture: a typology of agricultural regions
- Von Thunen model of agriculture
- भारत के कृषि प्रदेशों का उल्लेख करते हुए , किसी एक का विस्तारपूर्वक वर्णन कीजिये।
- व्हिटलसी द्वारा विश्व कृषि का वर्गीकरण | विश्व कृषि: कृषि क्षेत्रों की एक टाइपोलॉजी UPSC
1 Comments:
Click here for Commentsthank u so much...
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon