Plate tectonics is a theory that explains the dynamics of the outer lithosphere and it also explains the current position of continents and oceans and the location and development of various landforms such as mountains, plains, valleys, etc.
In 1967, the theory of plate tectonics was developed by Mackenzie, Parker, and Morgan.
According to the plate tectonics theory:
- The Earth's lithosphere [crust + uppermost layer of the mantle] is divided into several large and many smaller plates. The part divided by these is called a tectonic plate.
- If most of the plates are formed by continents, then it is called a continental plate otherwise it is called an oceanic plate.
- Oceanic plates are heavier and shallower than continental plates.
- The molten magma inside the lower layer of the mantle moves in a circular motion and forms many convection cells. These convection cells cause the movement of tectonic plates.
Changes in the Earth's crust are caused by two forces:
- Endogenous force
- Exogenous force
Plate tectonic theory explains the effects of endogenous forces on the Earth's crust and changes in the Earth's crust due to plate movement.
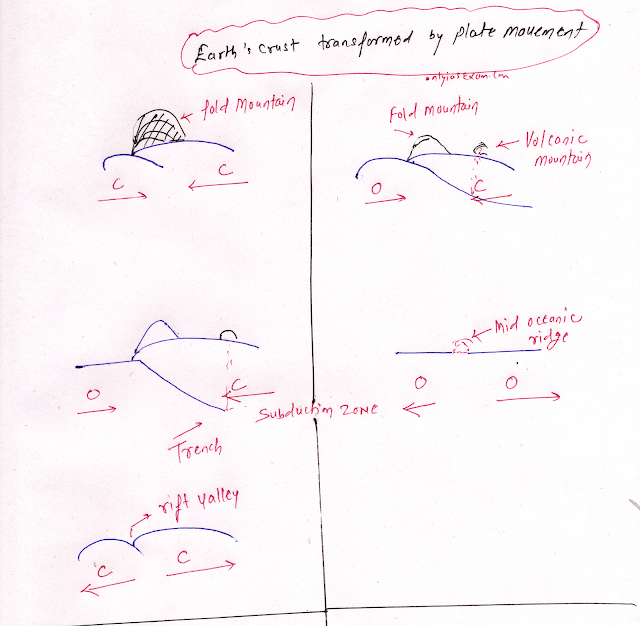
The movement of plates causes changes in the Earth's crust in the following ways:
- The Himalayan Mountains are formed at the convergence boundary of the Indian and Asiatic plates.
- Similarly, other fold mountains are formed either by the convergence of two continental plates or by the convergence of continental and oceanic plates. The Andes and the Rockies are formed at the boundary of oceanic and continental convergence.
- Volcanic islands are formed on the continent at the convergence boundary of oceanic and continental plates.
- Trenches are formed in the ocean and are formed at the convergence boundary of oceanic and continental plates. It also formed at the boundary of ocean and ocean convergence. A trench is formed when a heavier plate subducts under a lighter plate.
- Ocean ridges are formed at the divergence boundary of two oceanic plates. For example, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in the Atlantic Ocean is an example.
- Volcanic mountains or island arcs are formed at either convergence of two oceanic plates or at the convergence of oceanic and continental regions.
- Due to the divergence of plates, the distance between two continents or continents and oceanic, or two oceans, is increasing. Similarly, due to the convergence of the two plates, the distance between the plates is decreasing.
For example,
- The distance between Somalia and India is getting shorter.
- The Atlantic Ocean is expanding and the distance between Europe and America is increasing.
- Similarly, the Pacific Ocean is shrinking.
- What is plate tectonics? how do plate movements transform the earth's crust? ( 25 Marks, 66th BPSC geography Optional Paper)
- Bring about the basic difference between the drift theory and Plate tectonics. (UPPSC)
- Critically examine plate tectonics and explain its relation to the evolution of major landform features on the surface of the earth. ( BPSC, 2019)
- Describe the concept of plate tectonics and explain the effects of the collision of two similar and two dissimilar plates. ( UPPSC 2020)
- State the concept of plate tectonics. How does it help in explaining the formation of the Himalayas and the Appalachian Mountains? (UPSC 2014, 250 words, 20 marks)
You may like also:
- Describe the concept of plate tectonics and explain the effects of the collision of two similar and two dissimilar plates
- Critically examine plate tectonics and explain its relation to the evolution of major landform features on the surface of the earth.
- The Basic difference between the drift theory and Plate tectonics
- What is plate tectonics? how do plate movements transform the earth's crust?
- GEOSYNCLINES THEORY BY KOBER
- CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
- ISOSTASY IN GEOGRAPHY
- SEAFLOOR SPREADING
- PLATE TECTONICS THEORY (PTT)
- RECENT VIEWS ON THE MOUNTAIN BUILDING
- प्लेट विवर्तनिकी क्या है ? प्लेट संचलन कैसे भूपटल में बदलाव लाता है ?
- महाद्वीपीय विस्थापन सिद्धांत व प्लेट विवर्तनिकी सिद्धांत में मूलभूत अंतर बताये |
- प्लेट विवर्तनिकी के सिद्धांत का वर्णन कीजिये तथा दो समान एवं दो भिन्न प्लेटो के टकराव से होने वाले प्रभाव की व्याख्या कीजिये।
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon